Piezoceramic Materials

Piezo Materials Based on Lead Zirconate Titanate (PZT)
PI Ceramic provides a wide selection of piezoelectric ceramic materials based on modified lead zirconate titanate (PZT) and barium titanate. The designations of "soft" and "hard" piezo ceramics refer to the mobility of the dipoles or domains and hence also to the polarization and depolarization behavior. For actuator applications, ferroelectrically soft piezoceramics with low polarity reversal field strengths are used. Ferroelectrically hard PZT materials are primarily used in high-power acoustic applications. In addition, PI Ceramic offers lead-free piezo ceramics, currently used especially as ultrasonic transducers, and a crystalline actuator material.
For application-specific properties, actuators and transducers can be manufactured from special materials, although the technical implementation has to be checked individually.
The material properties are classified according to the EN 50324 European Standard.
Soft Piezoelectric Materials
Soft Piezoelectric Materials
Ideal for Piezo Actuators and Sensors
Ferroelectrically soft piezo ceramic materials can be polarized fairly easily even at relatively low field strengths. This is due to the comparably high domain mobility typical for them. The advantages of soft PZT materials are their large piezoelectric charge coefficient, moderate permittivities and high coupling factors.
Applications
Important fields of application for soft piezo ceramics are: Actuators for micropositioning and nanopositioning, sensors, such as conventional vibration detectors, ultrasonic transmitters and receivers, e.g., for flow or level measurement, object identification or monitoring, as well as for electro-acoustic applications as sound transducers and microphones, and also as sound pickups on musical instruments.
| PIC151 | Standard material for actuators of the PICA Stack/Thru and Piezo Tubes series |
|---|---|
| Material | Modified lead zirconate titanate |
| Characteristics | High permittivity, large coupling factor, high piezoelectric charge coefficient, relatively high Curie temperature |
| Suitable for | Actuators, low-power ultrasonic transducers, low-frequency sound transducers |
| Classification in accordance with EN 50324-1 | 600 |
| MIL-Standard DOD-STD-1376A | II |
| PIC255 | Standard material for PICA Power, DuraAct, PICA Shear, and Piezo Tubes series |
|---|---|
| Material | Modified lead zirconate titanate |
| Characteristics | Very high Curie temperature, moderate permittivity, high coupling factor, high charge coefficient, low mechanical quality factor, low temperature coefficient, relatively high polarity reversal field strength (>1 kV/mm) |
| Suitable for | Actuator applications for dynamic operating conditions and high ambient temperatures, low-power ultrasonic transducers, nonresonant broadband systems, force and acoustic pickup sensors |
| Classification in accordance with EN 50324-1 | 200 |
| MIL-Standard DOD-STD-1376A | II |
| PIC155 | |
|---|---|
| Material | Modified lead zirconate titanate |
| Characteristics | Very high Curie temperature, moderate permittivity, low mechanical quality factor, low temperature coefficient, high sensitivity (g coefficients) |
| Suitable for | Applications which require a high g coefficient (piezoelectric voltage coefficient), e.g., for microphones and vibration pickups with preamplifier, vibration measurements at low frequencies |
| Classification in accordance with EN 50324-1 | 200 |
| MIL-Standard DOD-STD-1376A | II |
| PIC153 | Material for special actuators of the PICA Stack/Thru series and for glued bending actuators |
|---|---|
| Material | Modified lead zirconate titanate |
| Characteristics | Extremely high permittivity and coupling factors, high charge coefficient, Curie temperature around 185 °C |
| Suitable for | Hydrophones, transducers in medical diagnostics and PZT translators |
| Classification in accordance with EN 50324-1 | 600 |
| MIL-Standard DOD-STD-1376A | VI |
| PIC152 | |
|---|---|
| Material | Modified lead zirconate titanate |
| Characteristics | Permittivity with extremely low temperature coefficient |
| Suitable for | Force and acceleration transducers |
| Classification in accordance with EN 50324-1 | 200 |
| MIL-Standard DOD-STD-1376A | II |
Hard Piezoelectric Materials
High-Performance Material for Ultrasonic Transducers
Ferroelectrically hard PZT materials can be subjected to high electrical and mechanical stresses. Their properties hardly change under these conditions.
The advantages of these materials are their moderate permittivity, large piezoelectric coupling factors, high mechanical qualities, and very good stability under high mechanical loads and operating field strengths. Low dielectric losses facilitate their continuous use in resonance mode with only low intrinsic heating of the component.
Applications
Especially high-power acoustic applications benefit from the properties of hard piezo materials. Examples of their fields of application include ultrasonic cleaning (typically in the kHz frequency range), the machining of materials (ultrasonic welding, bonding, drilling, etc.), ultrasonic processors (e.g., to disperse liquid media), the medical sector (ultrasonic tartar removal, surgical instruments, etc.) and sonar technology.
Material Properties and Classification
| PIC181 | |
|---|---|
| Material | Modified lead zirconate titanate |
| Characteristics | Extremely high mechanical quality factor, good temperature, and time stability of its dielectric and elasticity constants |
| Suitable for | High-power acoustic applications, resonance-mode ultrasonic applications |
| Classification in accordance with EN 50324-1 | 100 |
| MIL-Standard DOD-STD-1376A | I |
| PIC184 | |
|---|---|
| Material | Modified lead zirconate titanate |
| Characteristics | Large electromechanical coupling factor, moderately high quality factor, excellent mechanical and electrical stability |
| Suitable for | High-power ultrasound applications, hydroacoustics, sonar technology |
| Classification in accordance with EN 50324-1 | 100 |
| MIL-Standard DOD-STD-1376A | I |
| PIC144 | |
|---|---|
| Material | Modified lead zirconate titanate |
| Characteristics | Large electromechanical coupling factor, high quality factor, excellent mechanical and electrical stability, high compressive resistance |
| Suitable for | High-power ultrasound applications, hydroacoustics, sonar technology |
| Classification in accordance with EN 50324-1 | 100 |
| MIL-Standard DOD-STD-1376A | I |
| PIC241 | |
|---|---|
| Material | Modified lead zirconate titanate |
| Characteristics | High mechanical quality factor, higher permittivity than PIC181 |
| Suitable for | High-power acoustic applications, piezomotor drives |
| Classification in accordance with EN 50324-1 | 100 |
| MIL-Standard DOD-STD-1376A | I |
| PIC300 | |
|---|---|
| Material | Modified lead zirconate titanate |
| Characteristics | Very high Curie temperature |
| Suitable for | Use at temperatures up to 250 °C (briefly up to 300 °C) |
| Classification in accordance with EN 50324-1 | 100 |
| MIL-Standard DOD-STD-1376A | I |
Ideal for Applications with Impedance Matching
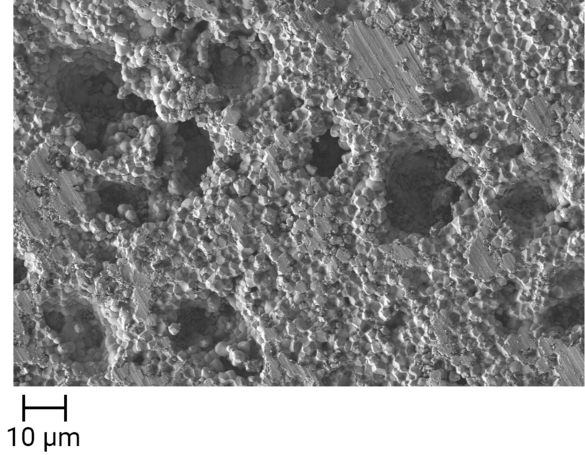

For applications where acoustic impedance matching is critical, we offer porous ceramics with reduced density. These materials function as impedance transformers, enabling optimal adaptation of the acoustic resistance between different media through carefully controlled porosity.
Thanks to their high specific surface area and application specific, optimized acoustic properties, they ensure maximum energy transfer while minimizing signal loss.
Different porosity levels and material densities, as well as the transfer of this technology to alternative materials, can be individually developed and customized upon request and technical evaluation.
Areas of Application
Porous ceramics are ideal for demanding applications, such as in underwater communication. They are also used in conventional vibration pickups, in ultrasonic transmitter and receiver systems for non destructive testing, in motion, pressure, and level sensors, as well as in medical, therapeutic, and surgical ultrasonic transducers, where they offer distinct performance and matching advantages.
| PIC255P63 | |
|---|---|
| Material | Modified lead zirconate titanate, PIC255 with 6,3 g/cm³ density |
| Characteristics | Low acoustic impedance, excellent acoustic matching to water, high piezoelectric coefficients, strong transmit and receive sensitivity, reduced density, larger specific surface area |
| Suitable for | Ultrasonic transducers with low power consumption, non‑resonant broadband systems, force and sound sensors, applications requiring impedance matching |
| Classification in accordance with EN 50324-1 | 200 |
| MIL-Standard DOD-STD-1376A | II |
Lead-Free Piezoelectric Materials
In addition to series components made of PZT, PI Ceramic also offers components made of >> lead-free materials from the bismuth sodium titanate (BNT) and potassium sodium niobate (KNN) systems. Currently, both systems include various materials at different levels of technological maturity. These are available for custom application developments.
There are only a few restrictions in shaping, so that a lead-free alternative is possible for a large number of lead-containing components in the corresponding basic geometry. Especially in resonant applications, lead-free piezoceramics can be an alternative to lead-containing materials. First positive development results can be demonstrated for, e.g., micropumps, ultrasonic nebulizers, and power ultrasonic transducers as well as sensors. Experience to date shows that lead-free materials behave differently in applications than PZT ceramics. For this reason, it is usually necessary to adjust the parameters and geometric dimensions for each application and to retest the long-term stability. This allows PI Ceramic to work with our customers to achieve the best application-specific results.
| Application | BNT Materials | KNN Materials | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PIC700 | PIC701 | PIC753 | PIC758 | ||
| Medical Technology | Nebulizers | xx | |||
| Sonication & Lysis | xx | ||||
| Mixing & Dispersion | xx | ||||
| Therapeutic & Surgical Utrasound | x | ||||
| Air Bubble Detection | xx | x | |||
| Flow Metering | xx | x | |||
| Industrial Applications | Material Processing | x | |||
| Flow Metering | xx | x | |||
| Hydro Acoustics | x | x | |||
| Level Sensors | x | ||||
| Ultrasonic Cleaning | x | ||||
| Non-Destructive Testing | x | x | |||
| Ultrasonic Sensors | x | ||||
| Ultrasonic Motors | x | ||||
Bismuth Sodium Titanate (BNT)
BNT materials are particularly well suited for thickness oscillation applications and perform well in the field of air bubble detection and flow sensor technology. For applications that utilize planar vibration, however, BNT materials are not suitable. The PI Ceramic BNT materials feature a high depolarization temperature. Therefore, unlike many other materials on the market, they can be processed by low-melting soldering or with thermosetting adhesives.
Potassium Sodium Niobate (KNN)
KNN components can also be easily soldered and bonded, but also have good planar properties compared to BNT components. They can therefore be used as an alternative to PZT components in air ultrasonic sensors, power ultrasonic transducers, nebulizer units, multilayer actuators, and ultrasonic motors.
For the manufacturing of piezo components, PI Ceramic uses only materials that have a better >> environmental footprint than PZT. PI Ceramic works with its customers to develop suitable components using lead-free materials.
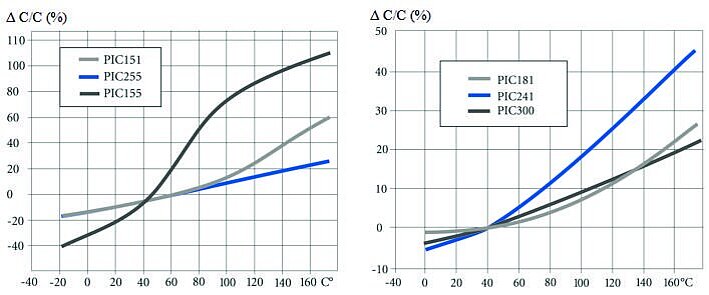
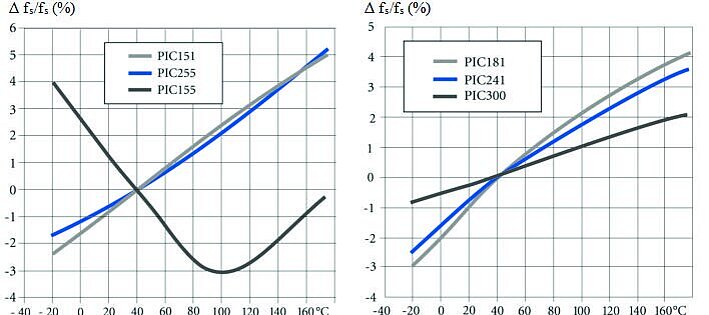
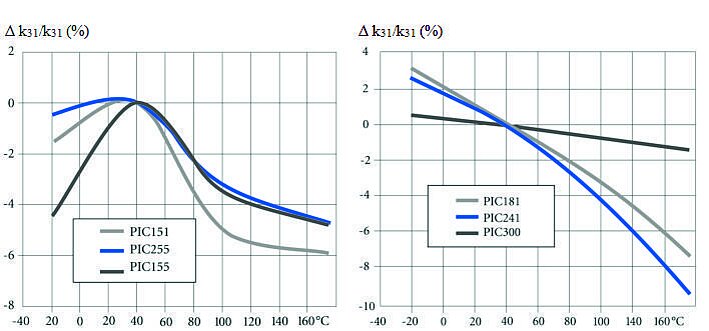
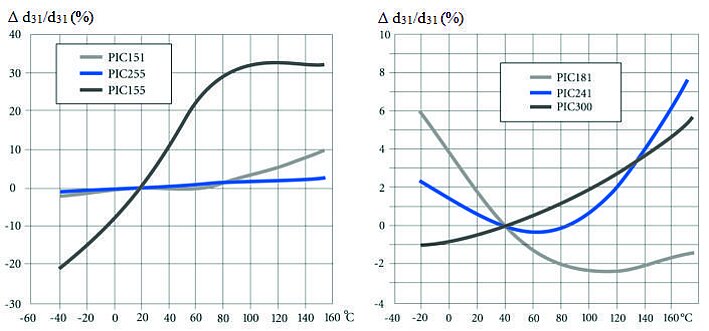
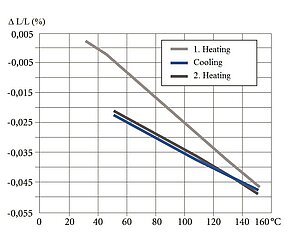
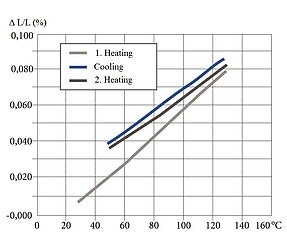
Thermal Properties Using PZT Ceramic PIC255 as Example
Thermal Properties Using PZT Ceramic PIC255 as Example
The thermal strain exhibits different behavior in the polarization direction and perpendicularly to it.
Nonpolarized piezoceramic elements are isotropic. The coefficient of expansion is approximately linear at a temperature coefficient of approx 2 × 10-6 / K.
The preferred orientation of the domains in a polarized PZT body leads to anisotropy, which is the cause of the varying thermal expansion behavior.
The effect of successive temperature changes must be taken into account in the application. Large changes in the curve can occur particularly in the first temperature cycle.
Depending on the material, it is possible that the curves deviate strongly from those illustrated.
| Material | PI Ceramic | Company A | Company B | Company C | Company D | Company E | Company F | Company G |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soft-PZT | PIC151 | Sonox P51 | 5600 | PZT5J-series | NCE56 | K500 | ||
| Soft-PZT | PIC152 | Sonox P502 | NCE53 | PZ23 | ||||
| Soft-PZT | PIC153 | 855 | Sonox P53 | 5700 | PZT5H1, PZT5H2 | NCE55 | PZ29 | K550 |
| Soft-PZT | PIC155 | |||||||
| Soft-PZT | PIC254 | Sonox P504 | ||||||
| Soft-PZT | PIC255 | 850 | Sonox P5 | 5500 | PZT5A-series | NCE51, NCE51f | PZ27, P188 | K350 |
| Hard-PZT | PIC144 | 840 | Sonox P4 | 5400 | PZT400 | NCE40, NCE41 | PZ26, P762 | K270 |
| Hard-PZT | PIC181 | 880 | Sonox P8, P88 | 5800 | PZT800 series | NCE80, NCE81 | PZ28, P189 | K278 |
| Hard-PZT | PIC184 | 840 | Sonox P4 | 5400 | PZT400 series | NCE40 | PZ26, P762 | K270 |
| Hard-PZT | PIC300 | Sonox P6 |
Downloads
Lead-Free Piezoceramic Materials
PI Ceramic RoHS Statement
Restriction of the use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment – RoHS 2011 / 65 / EU
Material Data
PI Piezoelectric Ceramic Products
Fundamentals, Characteristics and Applications
Piezoelectric Actuators
Components, Technologies, Operation
PI Ceramic REACH Regulation
Customer Information in Accordance with Article 33 (1) of the REACH Regulation